History of Chocolate
Chocolate may be the “food of the gods,” but for most of its 4,000-year history,
It was actually consumed as a bitter beverage rather than as a sweet edible treat. Anthropologists have found evidence that chocolate was produced by pre-Olmec c
ultures living in present-day Mexico as early as 1900 B.C. The ancient Mesoamericans who first cultivated cacao plants found in the tropical rainforests of Central America fermented, roasted and ground the cacao beans into a paste that they mixed with water, vanilla, honey, chili peppers and other spices to brew a frothy chocolate drink.
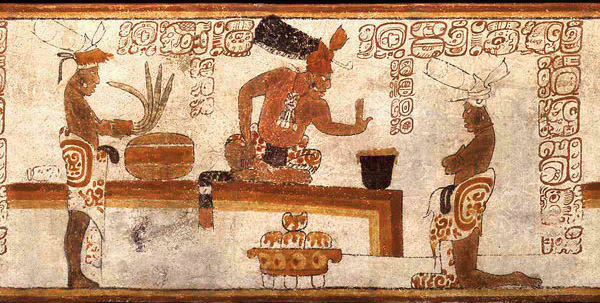
Olmec, Mayan and Aztec civilizations found chocolate to be an invigorating drink, mood enhancer and aphrodisiac, which led them to believe that it possessed
mystical and spiritual qualities. The Mayans worshipped a god of cacao and reserved chocolate for rulers, warriors, priests and nobles at sacred ceremonies.
When the Aztecs began to dominate Mesoamerica in the 14th century, they craved cacao beans, which could not be grown in the dry highlands of central Mexico that were the heart of their civilization. The Aztecs traded with the Mayans for cocao beans, which were so coveted that they were used as currency. (In the 1500s, Aztecs could purchase a turkey hen for 100 beans.) By some accounts, the 16th-century Aztec emperor Montezuma drank three gallons of chocolate a day to increase his libido.
In the 1500s, Spanish conquistadors such as Hernán Cortés who sought gold and silver in Mexico returned instead with chocolate. Although the Spanish sweetened the bitter drink with cane sugar and cinnamon, one thing remained unchanged: chocolate was still a delectable symbol of luxury, wealth and power. Chocolate was sipped by royal lips, and only Spanish elites could afford the expensive import.

Spain managed to keep chocolate a savory secret for nearly a century, but when the daughter of Spanish King Philip III wed French King Louis XIII in 1615, she brought her love of chocolate with her to France. The popularity of chocolate quickly spread to other European courts, and aristocrats consumed it as a magic elixir with salubrious benefits. To slake their growing thirst for chocolate,
European powers established colonial plantations in equatorial regions around the world to grow cacao and sugar. When diseases brought by the European explorers depleted the native Mesoamerican labor pool, African slaves were imported to work on the plantations and maintain the production of chocolate.